AMR Spread
Welcome to the AMR Spread user interface!
Using a mechanistic deterministic multi-country model of the transmission of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, simulate the spread of an emergent carbapenem-resistant E. coli worldwide.
|
Select the emergent resistant E. coli characteristics, national antibiotic consumption levels, international travel flows and index country where emergence starts. Then, simulate for 20 years the emergence corresponding to the selected scenario. After simulation, visualize two outputs: |
AMR Model
MODEL USED FOR SIMULATIONS
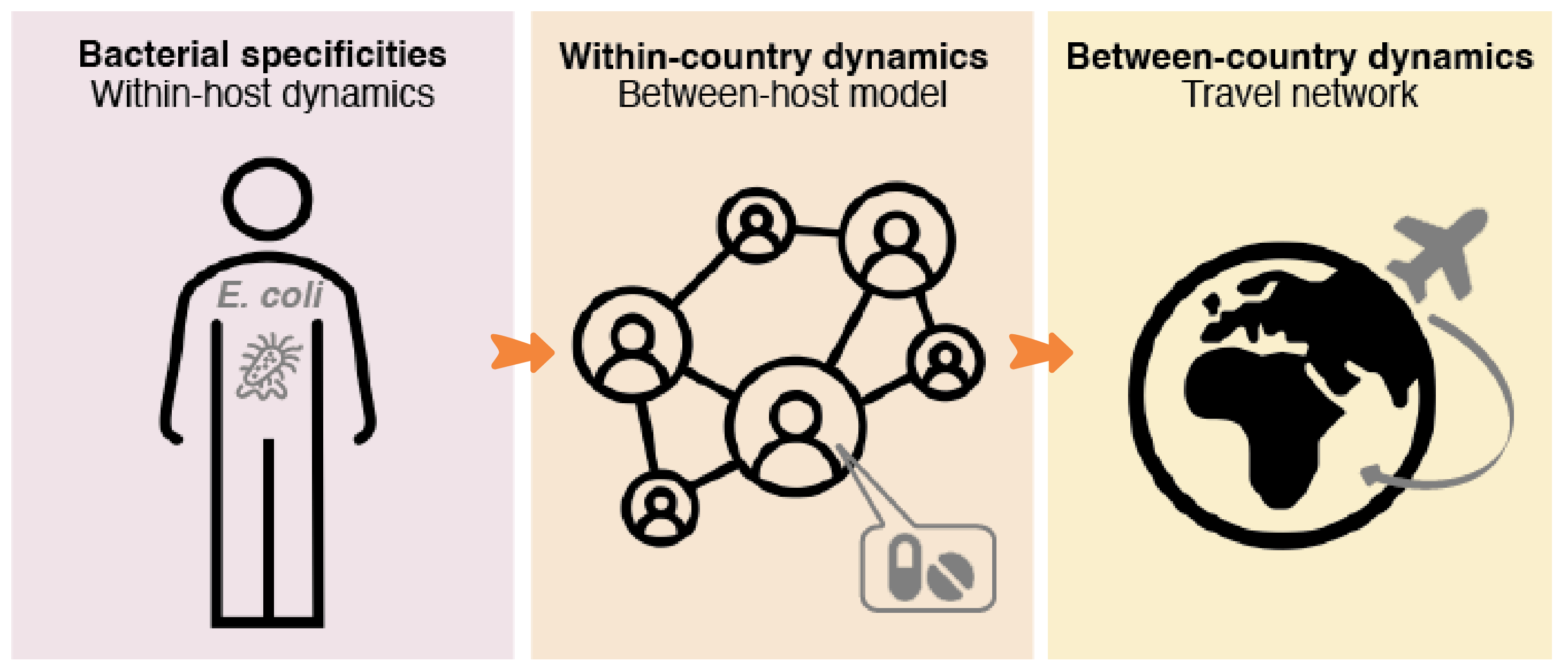
We build a mechanistic deterministic between-host model of the transmission of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli. The model is calibrated using empirical data of endemic ESBL-producing E. coli. Then, the model is used to simulate the spread of an emergent resistant bacteria worldwide, such as carbapenem-resistant E. coli.
The model is initialized by defining the characteristics of an emerging resistant bacterium, which is introduced at the start of the simulation in a given index country. National antibiotic consumption levels in every country and travel fluxes between every country can be varied. The model simulates, over 20 years, the spread of the emerging resistant bacteria between individuals within a country, and between different countries connected by travel flows. A "simulation" thus corresponds to the spread of an emerging resistant bacterium from an index country to other countries over time.
Schematic of the between-host model used for simulations
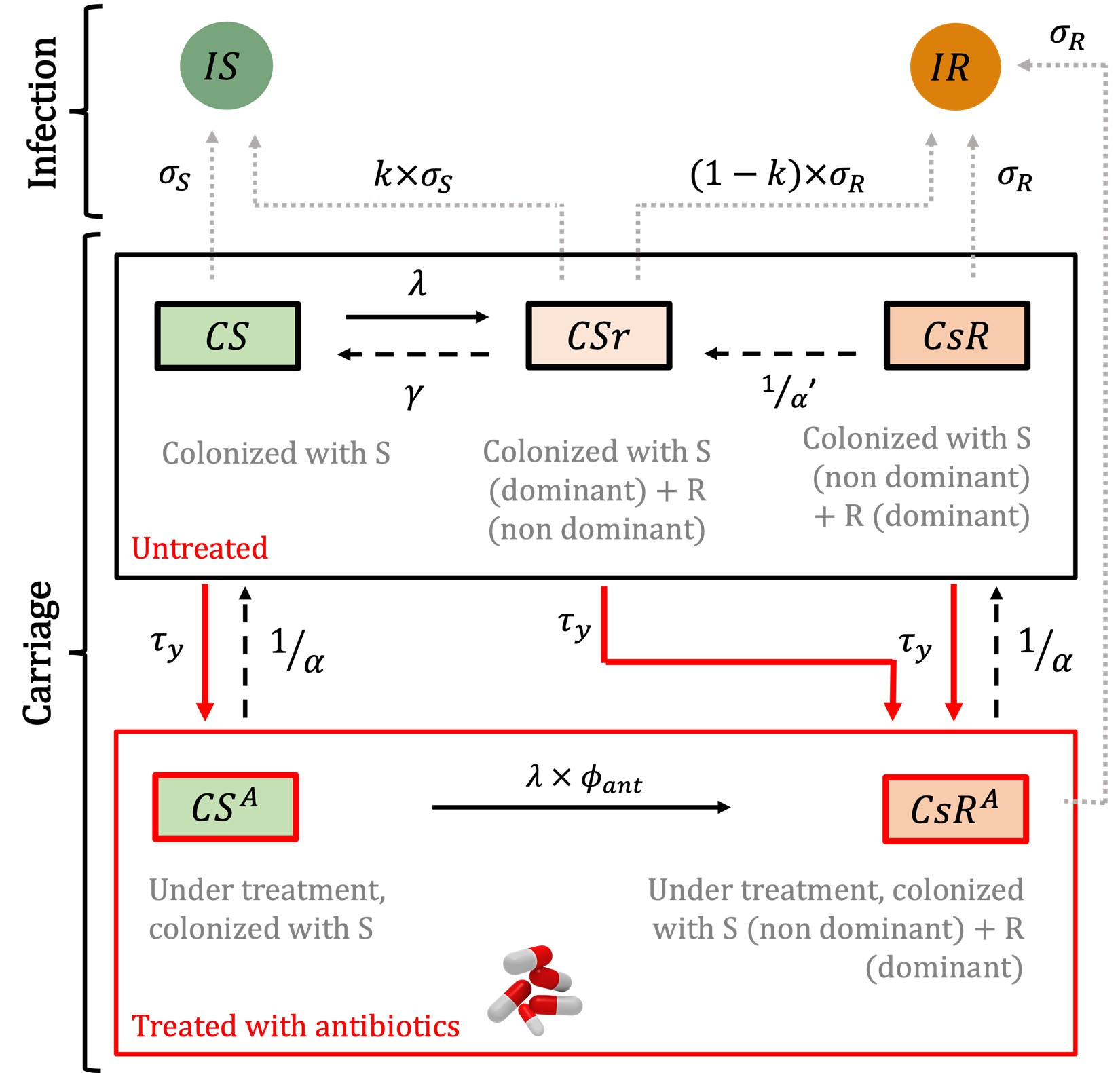
EQUATIONS FOR THE MODEL
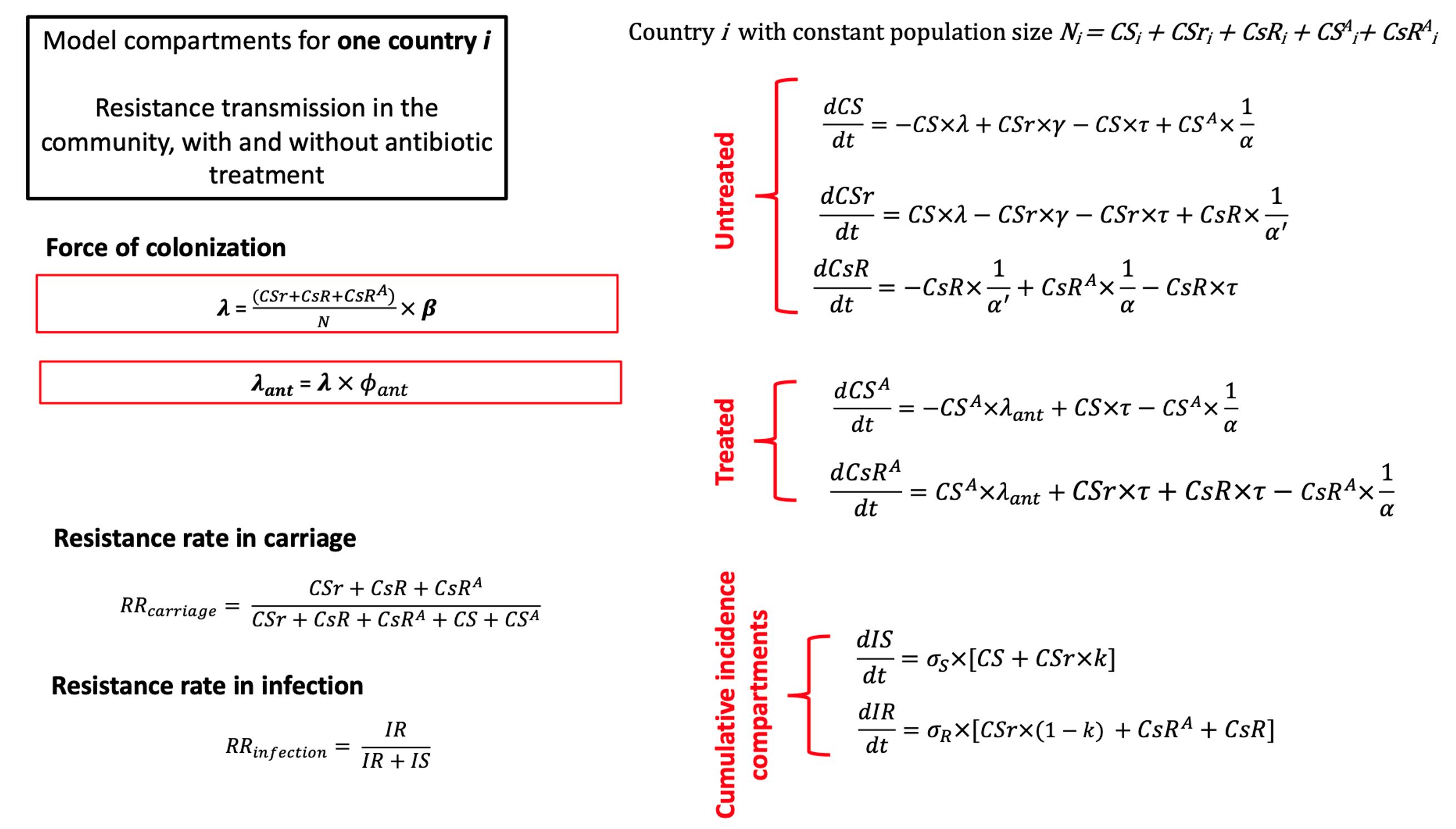
INPUT PARAMETERS
|
|
|
|
|
|
| NORMAL BUG SCENARIO |
SUPER BUG SCENARIO |
FITNESS COST BUG SCENARIO |
MULTI-DRUG RESISTANT BUG SCENARIO |
|
| βi | Estimated per country | βi x 1.1 | βi x 0.9 | |
| σS i | Estimated per country | |||
| ai | Estimated per country | |||
| σR i | σR i = ai x σS i | |||
| α | 8 days | |||
| α' | 60 days | |||
| γ | 1/120 days-1 | |||
| φant | 9.83 | |||
| k | 0.80 | |||
| τy,i |
Carbapenems treatment rate per year y and country i
Data source: IQVIA |
Carbapenems and β-lactams treatment rate per year y and country i
Data source: IQVIA |
||
| Δy,i,j |
travel matrix (% of inhabitants of country i traveling to country j per year y)
Data source: KCMD |
INITIAL CONDITIONS
CS = Ni x (1 - τ1,i)
CSr = n
CsR = 0
CSA = Ni x (τ1,i)
CsRA = 0
Ni is population size of country i (data: World Bank)
n is initial number of resistant bacteria carriers at the beginning of the simulation (n = 1000)
Data
DATA USED FOR SIMULATIONS
Antibiotic resistance data: Model calibrated using antibiotic resistance data from the Pfizer ATLAS database. https://atlas-surveillance.com/#/login
Antibiotic consumption data: Synthetic data representing trends of antibiotic consumption by country and by year.
Travel data: Data obtained from the Knowledge Center for Migration and Demography (KCMD) data hub, from the Global Transnational Mobility dataset. Data represent the estimated number of travelers country by country,
for year periods between 2011-2016.
https://migration-demography-tools.jrc.ec.europa.eu/data-hub/
Contact
TEAM

Eve Rahbé
Doctorante en biostatistiques santé publique, Paris-Saclay
Equipe Epidémiologie et Modélisation de l’échappement aux anti-infectieux, Institut Pasteur, INSERM

Philippe Glaser
Directeur de recherche
Equipe Ecologie et Evolution de la résistance aux antimicrobiens,
Institut Pasteur

Lulla Opatowski
Professeure, Chercheure-enseignante, UVSQ
Equipe Epidémiologie et Modélisation de l’échappement aux anti-infectieux, Institut Pasteur, INSERM
HOME PAGE TEAM/PROJECT
Credits
CONTRIBUTORS

Eve Rahbé
Author of simulation code
PhD Student in biostatistics public health, Paris-Saclay
Epidemiology and modelling of antibacteiral evasion(EMAE) team, Institut Pasteur, INSERM

Elodie Chapeaublanc
elodie.chapeaublanc@pasteur.fr
Implementation and Deployment
Research Engineer - Web Developer
Head of Web INTERface Group
Hub Bioinformatique et Biostatistique,
Institut Pasteur, Paris

Rachel Torchet
Develop User Interface
Research Engineer - UX/UI Designer
Hub Bioinformatique et Biostatistique,
Institut Pasteur, Paris
TECHNICAL IMPLEMENTATION DETAILS
The website was developed in R Shiny and deployed on Kubernetes cluster of Institut Pasteur.


